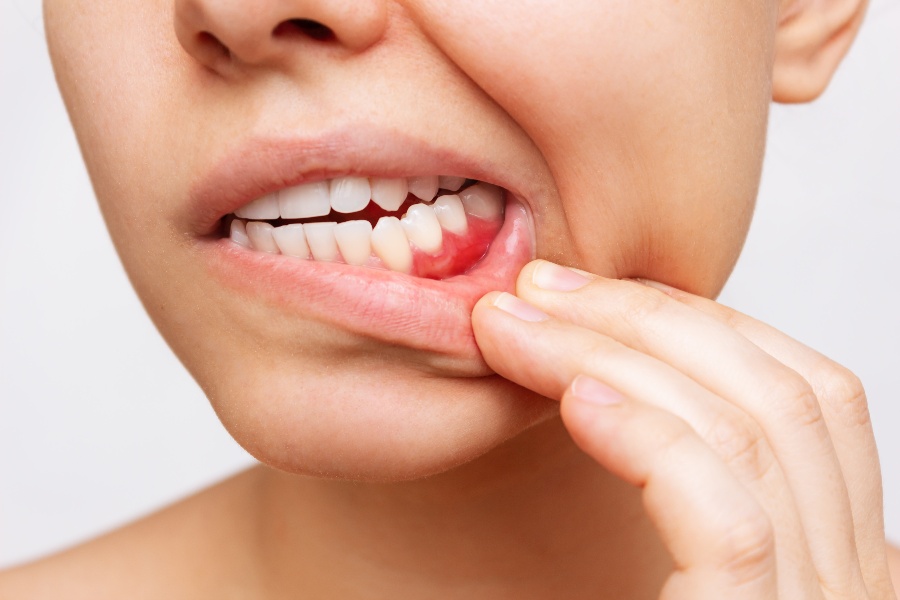
Healthy gums are essential to your oral health. While you can take the necessary precautions, like brushing twice a day and following other oral hygiene practices, your gums may still bleed occasionally.
Frequently bleeding gums can be caused by a number of different factors and issues and may also be an indication of more serious underlying conditions this article discusses seven possibilities to consider that may be the reason for your bleeding gums and steps you can take to resolve the issue.
Common Reasons Why Gums Bleed
Gums can bleed for various reasons, including:
1. Brushing Too Hard
Brushing your teeth properly can help you maintain oral hygiene. However, some people brush too vigorously for various reasons. Some individuals believe that brushing their teeth harder can help them remove all the plaque. Cleaning your teeth using the wrong toothbrush type or too roughly can irritate your gums and cause bleeding. To reduce irritation and bleeding:
- brush your teeth in gentle, circular motions
- switch to a toothbrush with soft bristles
- if your gums are sensitive, find a toothpaste made for sensitive teeth
- if you have bleeding gums when you floss, find a softer floss or consult your dentist regarding water flossers and interdental brushes
If your gums bleed because of flossing or brushing, the bleeding is often temporary and stops when your gums get a chance to heal.
2. Gingivitis (Gum Disease)
Gum disease or gingivitis is the most common cause of bleeding gums. Gingivitis can cause tender, swollen, and sometimes bleeding gums while brushing one's teeth. This condition is the first phase of gum disease or periodontal disease. When you don't remove the plaque at your gum line and on your teeth by flossing and brushing, it can infect your gums and make them sensitive or prone to bleeding.
The silver lining is that gingivitis can be reversible by improving your oral hygiene and visiting a dentist to get professional cleaning and dental hygiene treatments. If you don't treat gingivitis, it can evolve into severe periodontitis, which can cause permanent teeth damage or tooth loss.
If your dentist diagnoses your gingivitis, it may interest you to know that gum disease can affect other health issues. The American Academy of Periodontology asserts that diabetes is a risk factor for gingivitis. Some individuals' gingivitis can cause other severe ailments, such as stroke and heart disease.
3. Vitamin Deficiencies
Low vitamin K or C levels in your bloodstream can increase your susceptibility to bleeding gums. A simple blood test can be performed by your primary care physician to detect your vitamin levels and assess any deficiencies. If the check reveals you do have a vitamin deficiency, you may be able to improve your levels through your diet or supplements.
You can consume various food to increase your vitamins C and K intake. Consider incorporating these items into your diet to ensure you are getting the necessary nutrients. Vegetables and fruits that contain significant amounts of vitamin C are:
- tomatoes
- broccoli
- potatoes
- bell peppers
- citrus fruits
- strawberries
Leafy greens that are excellent sources of vitamin K are:
- watercress
- lettuce
- kale
- spinach
- mustard greens
Other ideal sources of vitamin K are canola oil, soybeans, and olive oil.
4. Hormone Changes
During menopause, puberty, or pregnancy, hormone fluctuations can increase blood flow to one's gums, making the gums sensitive or prone to bleeding. Pregnant individuals are at a higher risk of gum diseases, a common cause of gums bleeding. The American Pregnancy Association refers to this as "pregnancy gingivitis."
This condition is often temporary, provided you maintain proper oral hygiene to prevent gum disease. Brush or floss gently and avoid touching your gums if they bleed easily or are sensitive. You may also visit your dentist and schedule dental hygiene appointments to manage gum inflammation or bleeding.
5. Medications and Health Conditions
Some health problems may also increase your susceptibility to bleeding gums. For example, bleeding disorders like leukemia or hemophilia and infections like herpes simplex virus can increase your risk of bleeding gums.
Taking some blood-thinning medications may also make your gums susceptible to bleeding. These drugs can include some types of aspirin, warfarin, and heparin.
Consult your doctor if you're worried that your bleeding gums can be a symptom of an illness. Your physician can also advise you whether a change of medication is necessary.
Managing these potential causes of bleeding gums can help you control your bleeding gums, protecting you from severe health issues.
6. Poorly Fitted Braces or Dentures
Braces, dentures, and other dental or orthodontic devices can sometimes cause bleeding gums. The fittings can make your gums bleed if they're too tight, loose, or dislodged. You may be more susceptible to bleeding gums if your gums are sensitive.
During your regular dental check-ups, your dentist can check whether your braces or dentures fit well. If they aren't fitted properly, the dentist can make the necessary adjustments, such as loosening or tightening braces and replacing or realigning dentures.
If you're worried about a painful or poorly fitting oral device, schedule an appointment to see a dentist immediately. Prolonging your visit can worsen the problem and deny you the necessary urgent medical care.
7. Bleeding After a Dental Injury or Treatment
Bleeding gums may be common after a dental procedure like wisdom teeth removal, oral surgery, or tooth extraction. Your gums may also continue to bleed after an injury to your mouth. This bleeding is often temporary, and can usually be relieved by applying a clean cloth at intervals of about half an hour.
Don't eat, drink, or rinse your mouth until the bleeding stops. Once the bleeding stops, avoid smoking and touching the wound while the gum heals. If the bleeding persists, visit an ER or contact an emergency dentist.
Understanding Gum Disease
Gum disease is the most common cause of bleeding gums. Its early stage is gingivitis, characterized by red, swollen, or sore gums. These gums can bleed as you floss or brush your teeth. Untreated gingivitis can develop into periodontitis. The signs of periodontitis are:
- receding gums
- unpleasant taste in your mouth or bad breath
- sensitive or painful teeth, particularly when biting
- teeth feeling loose
Gum disease can affect your gums' healing ability, increasing your risk for complications after dental procedures. The condition can also make you unfit for treatments like cosmetic dental procedures, such as teeth whitening. Visiting a dentist can help you overcome your gum disease.
Palmetto Dental Arts offers a full range of dental services to clients in Bluffton and the surrounding areas. Our team offers a number of different specialties enabling us to provide advanced restorative and surgical dental treatments from start to finish all under one roof. Book an appointment today to get the help you need to overcome gum disease or bleeding gums.