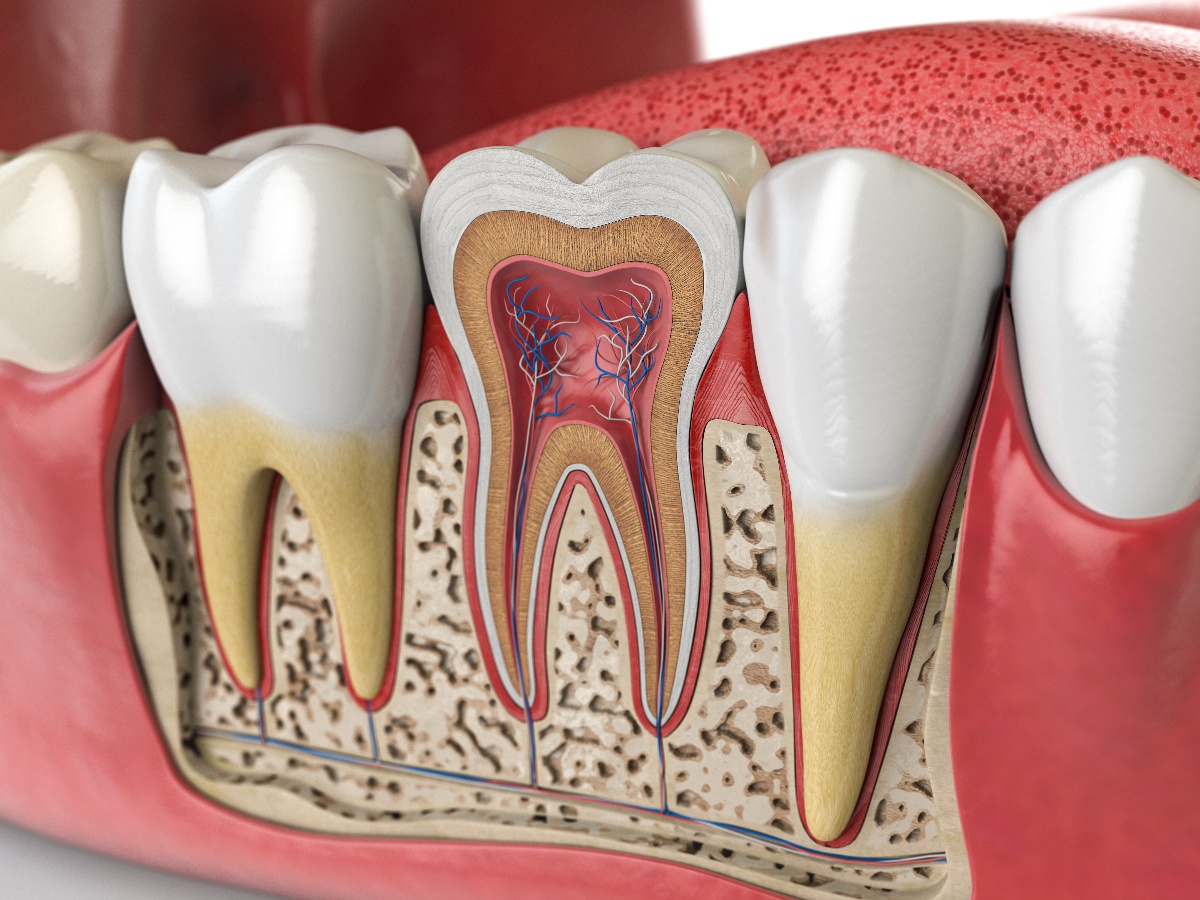
We all know that Vitamin D is essential for strong bones, but we now know that you need healthy Vitamin D levels to maintain healthy teeth and gums healthy? It may be time to rethink Vitamin D, commonly called the “sunshine vitamin,” as more than essential for bone health. Emerging research suggests that its influence on oral health may be as significant as its impact on our skeletal system.
Just as Vitamin D helps our bodies absorb calcium to build and maintain strong bones, it also appears to help strengthen teeth and support the health of our gums. This connection is becoming increasingly clear as scientists continue to research the complex relationship between nutrition and oral health.
What Is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D isn't your typical vitamin; it's actually a fat-soluble vitamin that functions more like a hormone in the body. Unlike most vitamins, which we primarily get from food, Vitamin D has a unique double identity. Direct sunlight causes production of Vitamin D in your skin. But you can also obtain it through diet.
The process of making Vitamin D is quite fascinating. When sunlight hits our skin, it triggers a chemical reaction that converts a cholesterol derivative into a precursor of Vitamin D. This precursor then undergoes further transformations in the liver and kidneys, ultimately becoming the active form of Vitamin D that our bodies can use.
However, sunlight isn't the only way to get this vital nutrient. Certain foods, such as fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel), egg yolks, and fortified dairy products, contain naturally occurring Vitamin D.
It's worth noting that there are two main types of Vitamin D:
- Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol): This type is primarily found in plant-based foods and supplements.
- Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol): This type is produced in our skin from sunlight and is also found in animal-based foods and supplements.
While both types can raise Vitamin D levels in the body, research suggests that Vitamin D3 might be more effective in maintaining optimal levels. However, the best way to ensure you're getting enough Vitamin D is to discuss your individual needs with your healthcare provider.
Vitamin D and Tooth Development
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in tooth development, particularly during the early stages of life. Its primary function in this process is closely tied to its ability to regulate calcium and phosphorus metabolism, two minerals essential for building strong teeth.
One of the most significant ways vitamin D contributes to tooth development is through its role in calcium absorption. When vitamin D levels are adequate, the body can more efficiently absorb calcium from the diet, ensuring that developing teeth have access to this vital mineral. This process is particularly important during the formation of tooth enamel, the hardest tissue in the human body.
The impact of vitamin D on tooth development extends beyond just calcium absorption. It also:
- Stimulates the production of dentin, the layer beneath the enamel
- Helps in the mineralization of tooth structures
- Supports the development of a healthy tooth root
- Influences the formation of tooth buds in infants
Adequate vitamin D levels during pregnancy and early childhood are especially critical for proper tooth development. Studies have shown that children born to mothers with vitamin D deficiency may have an increased risk of enamel defects and early childhood caries.
Furthermore, vitamin D continues to play a role in maintaining tooth strength throughout life. It helps in the ongoing process of remineralization, where minerals are redeposited into the tooth enamel after exposure to acids from food or bacteria. This constant renewal process is crucial for maintaining the integrity and strength of tooth enamel over time.
By understanding the fundamental role of vitamin D in tooth development, we can appreciate why maintaining adequate levels of this nutrient is essential not just for overall health, but specifically for the strength and longevity of our teeth.
Vitamin D and Dental Caries Prevention
Vitamin D plays a significant role in preventing dental caries, commonly known as tooth decay. Its impact on caries prevention is multifaceted, involving several mechanisms that work together to protect teeth from decay.
One of the primary ways vitamin D helps prevent dental caries is through its influence on tooth mineralization. By promoting calcium absorption and incorporation into tooth structures, vitamin D helps maintain and strengthen tooth enamel. This stronger enamel is more resistant to acid attacks from bacteria, which is the primary cause of tooth decay.
Vitamin D also impacts saliva production and composition, which is crucial for maintaining oral health. Adequate vitamin D levels contribute to:
- Increased saliva production, which helps neutralize acids in the mouth
- Enhanced calcium and phosphate content in saliva, aiding in remineralization
- Improved buffering capacity of saliva, helping to maintain optimal pH levels in the oral cavity
- Promotion of antimicrobial peptide production in saliva, providing natural defense against harmful bacteria
Furthermore, vitamin D has been found to have antibacterial properties that directly impact the oral microbiome. It can help reduce the growth of cariogenic bacteria, particularly Streptococcus mutans, which is the primary bacteria responsible for tooth decay.
Research has shown that individuals with higher vitamin D levels tend to have a lower incidence of dental caries. A systematic review of clinical studies found that vitamin D supplementation was associated with a 47% reduction in the incidence of dental caries.
It's important to note that while vitamin D plays a crucial role in caries prevention, it works best in conjunction with good oral hygiene practices and a balanced diet low in sugary foods. By ensuring adequate vitamin D intake alongside these other preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing dental caries and maintain healthier teeth over their lifetime.
Vitamin D and Periodontal Health
Vitamin D's influence on oral health extends beyond tooth structure to play a vital role in maintaining healthy gums and supporting tissues. Its impact on periodontal health is significant and multifaceted, contributing to the overall integrity of the oral cavity.
One of the primary ways vitamin D supports periodontal health is through its role in maintaining healthy gum tissue. Vitamin D receptors are present in gum tissue cells, indicating its direct involvement in gum health. Adequate vitamin D levels help:
- Promote gum tissue integrity and repair
- Enhance the natural defense mechanisms of gum tissues
- Support the healing process in case of gum injuries or infections
- Reduce gingival inflammation
Perhaps even more crucial is vitamin D's effect on alveolar bone density. The alveolar bone is the portion of the jawbone that supports and anchors the teeth. Vitamin D, working in concert with calcium, is essential for maintaining and improving bone mineral density. This is particularly important in preventing and managing periodontal disease, as bone loss is a hallmark of advanced periodontitis.
Vitamin D also exhibits potent anti-inflammatory properties, which are beneficial for periodontal health. Chronic inflammation is a key factor in the progression of periodontal disease. By modulating the immune response and reducing inflammation, vitamin D can help:
- Mitigate the destructive effects of chronic gum inflammation
- Regulate the production of inflammatory cytokines
- Support a balanced immune response in the oral cavity
Studies have shown a correlation between vitamin D deficiency and an increased risk of periodontal disease. Conversely, individuals with higher vitamin D levels tend to have better periodontal health and a lower risk of gum disease progression.
It's worth noting that while vitamin D plays a crucial role in periodontal health, it's most effective when combined with good oral hygiene practices, regular dental check-ups, and a healthy lifestyle. By ensuring adequate vitamin D intake, individuals can provide their gums and supporting structures with an additional layer of protection against periodontal disease.
Vitamin D Deficiency and Oral Health Issues
Vitamin D deficiency can have significant implications for oral health, potentially leading to a range of dental and periodontal problems. Recognizing the signs of deficiency and understanding its impact on oral health is crucial for maintaining a healthy mouth.
Common signs of vitamin D deficiency that may manifest in the oral cavity include:
- Delayed tooth eruption in children
- Increased susceptibility to dental caries
- Softening of tooth enamel (hypomineralization)
- Periodontal inflammation and bleeding gums
- Weakened alveolar bone structure
- Increased tooth sensitivity
One of the most significant consequences of vitamin D deficiency is an increased risk of dental caries. Without adequate vitamin D, the body struggles to absorb and utilize calcium effectively, leading to weaker tooth enamel that's more susceptible to decay. Studies have shown that individuals with low vitamin D levels are at a higher risk of developing cavities, particularly in children and adolescents.
Vitamin D deficiency also significantly impacts periodontal health. Insufficient vitamin D levels can lead to:
- Reduced alveolar bone density, increasing the risk of tooth loss
- Impaired immune response, making gum tissues more vulnerable to infections
- Chronic gum inflammation, potentially accelerating the progression of periodontal disease
Furthermore, vitamin D deficiency can exacerbate existing oral health conditions. For instance, individuals with periodontal disease who are also deficient in vitamin D may experience more rapid bone loss and a poorer response to periodontal treatments.
It's important to note that vitamin D deficiency often develops gradually and may not present obvious symptoms in its early stages. Regular dental check-ups can help identify potential signs of deficiency, allowing for early intervention. Additionally, if you're concerned about your vitamin D levels, consult with your healthcare provider about getting a blood test to assess your vitamin D status.
Addressing vitamin D deficiency through appropriate dietary changes, safe sun exposure or supplementation under medical guidance can significantly improve overall oral health and reduce the risk of dental and periodontal issues.
Optimizing Vitamin D Intake for Dental Health
Ensuring adequate vitamin D levels is crucial for maintaining optimal dental health. While the body can produce vitamin D through sun exposure, many people may not get enough sunlight or may have factors limiting their vitamin D synthesis. Therefore, it's important to consider various sources and methods to optimize vitamin D intake.
Dietary sources rich in vitamin D include:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna)
- Egg yolks
- Cheese
- Beef liver
- Fortified foods (milk, orange juice, cereals)
- Mushrooms exposed to UV light
While these foods can contribute to vitamin D intake, it can be challenging to obtain sufficient amounts solely through diet, especially for individuals with dietary restrictions or limited food choices.
Safe sun exposure is another way to boost vitamin D levels. However, it's important to balance the benefits of vitamin D production with the risks of excessive UV exposure. Guidelines for safe sun exposure include:
- Aim for short periods of sun exposure, typically 10-30 minutes, several times a week
- Expose larger areas of skin, such as arms and legs
- Avoid peak sun hours (10 am to 4 pm) to reduce the risk of sunburn
- Consider factors like skin tone, latitude, and season, which can affect vitamin D production
For many individuals, especially those living in northern latitudes or with limited sun exposure, vitamin D supplementation may be necessary. When considering supplementation:
- Consult with a healthcare provider to determine your appropriate dosage
- Choose between vitamin D2 or D3 supplements (D3 is generally considered more effective)
- Consider combination supplements that include both vitamin D and calcium
- Be aware of potential interactions with medications or health conditions
It's important to note that while optimizing vitamin D intake is beneficial for dental health, it should be part of a comprehensive approach to oral care. This includes maintaining good oral hygiene practices, regular dental check-ups, and a balanced diet low in sugary and acidic foods.
By taking steps to ensure adequate vitamin D levels through a combination of diet, safe sun exposure, and appropriate supplementation when necessary, individuals can support their dental health and contribute to stronger teeth and healthier gums.
Schedule an Appointment
To learn more about how Palmetto Dental Arts can help you maintain healthy teeth and gums, call us or contact us online.