Prevention, early detection, and timely treatment are critical to maintaining healthy gums. Dentists typically emphasize regular checkups because early gum disease can be reversed with proper care. Keeping your gums healthy can save you from the potential discomfort and serious consequences of advanced periodontal disease.
The Vital Role of Your Gums
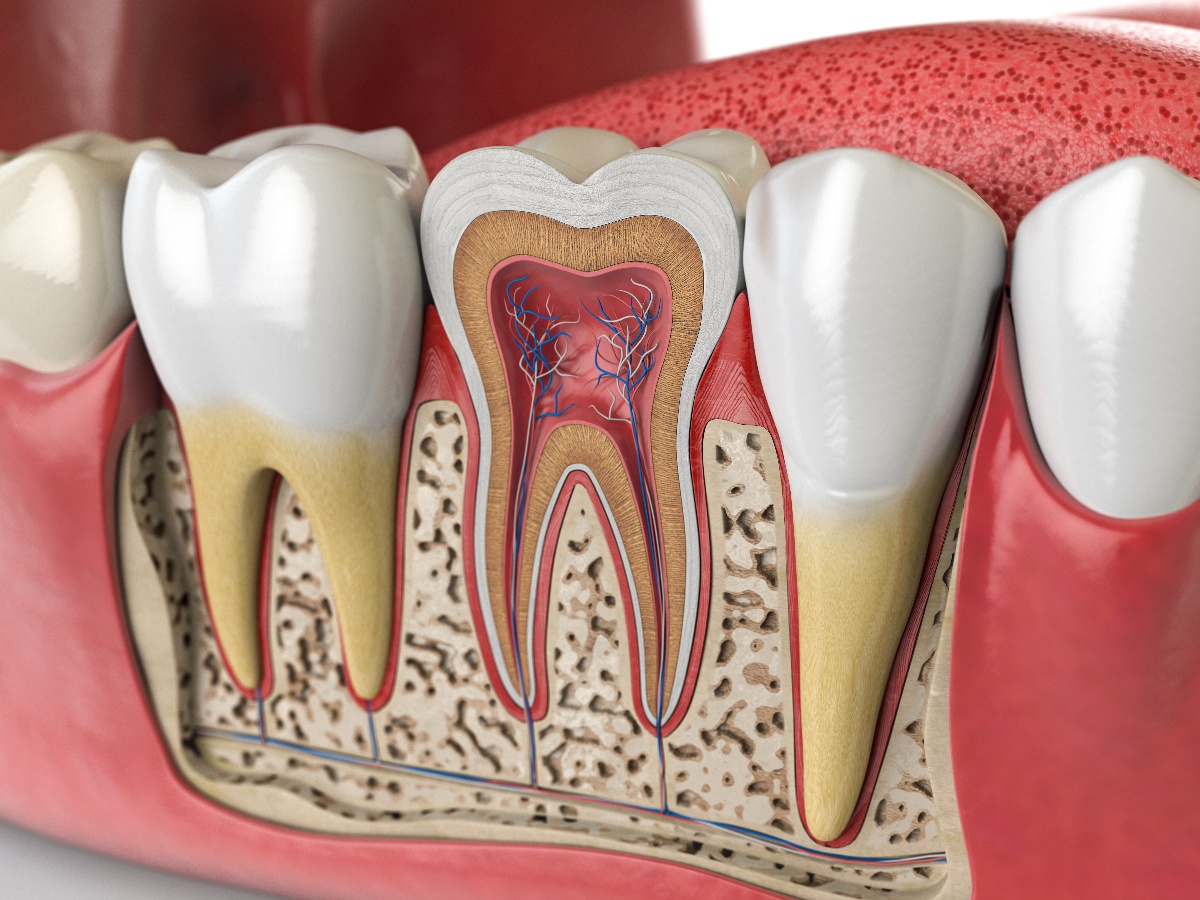
When it comes to your oral health, the importance of your gums cannot be overstated. Although most people focus on having straight white teeth for a bright smile, your gums are critical in helping you eat, speak, and smile confidently. The vital functions of your gums include the following:
- Protection. Your gums act as a protective barrier to prevent harmful bacteria from affecting the underlying jawbone and tooth roots. This is especially important for your teeth because roots are at a higher risk for tooth decay than the crowns, or upper part, of your teeth.
- Support. The gums hold your teeth firmly in place, helping to maintain alignment and absorb forces during chewing.
- Aesthetics. Healthy gums contribute significantly to your smile's appearance by shaping your teeth's appearance. Additionally, the light pink color of health gums optimally frames your teeth for a bright and appealing smile.
- Sensory Function. Gums serve a sensory function to alert you to potential oral health problems such as inflammation or periodontitis. Gums also help regulate your bite pressure, making it possible to chew food effectively.
- Nutritional Supply. The blood vessels in your gums help supply essential nutrients and oxygen to the tooth roots and surrounding tissues.
- Speech. Healthy gums contribute to clear speech by keeping your teeth strong and stable.
The Critical Importance of Healthy Gums
Healthy gums are a cornerstone of oral health, acting as the first line of defense against bacterial infections and providing support for your teeth. They play a critical role in preventing the onset of oral diseases such as gingivitis and periodontitis, conditions that can lead to more serious issues like tooth loss if left untreated.
The health of your gums also influences other aspects of your oral health. For instance, receding gums can expose a tooth's root, leading to increased sensitivity and cavities. Additionally, healthy gums contribute significantly to your smile's aesthetics, giving you the confidence to smile brightly.
In addition to their role in oral health, your gums are also a window into your overall health. Interestingly, a growing body of research suggests that your oral health, particularly the health of your gums, may have far-reaching implications for your overall health. A number of systemic diseases - those that affect your entire body - have been linked to gum health.
Here are some systemic conditions that research suggests may be linked to gum health:
- Cardiovascular Disease. Recent research has shown a connection between gum disease and heart disease, possibly due to inflammation. It's also suggested that oral bacteria can contribute to the formation of clots and plaque build-up in arteries.
- Diabetes. Gum disease appears more frequently and is usually more severe among people with diabetes. Uncontrolled blood sugar levels can elevate your risk of gum disease, and severe gum disease can affect blood glucose control.
- Respiratory Infections. Bacteria resulting from gum disease can be inhaled or travel to the lungs, potentially causing respiratory diseases like pneumonia.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis. There's a potential link between gum disease and rheumatoid arthritis due to their shared inflammatory response.
- Alzheimer's Disease. Long-term gum inflammation may contribute to the development of Alzheimer's disease by possibly causing inflammation in the brain.
- Osteoporosis. This condition can affect the bones in the jaws, potentially leading to tooth loss in the presence of gum disease.
- Cancer. Some research has linked gum disease to certain types of cancer, including oral, pancreatic, and lung cancer.
- Pregnancy Complications. Gum disease in pregnant women possibly increases the risk of some complications at birth.
Types of Gum Disease
The main types of gum disease are:
Gingivitis. This early gum inflammation is the earliest and mildest form of gum disease. It is caused by plaque build-up on teeth, leading to gum inflammation. Fortunately, gingivitis can be reversed with good oral hygiene and regular professional dental cleanings.
Periodontitis. Without treatment, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis which can cause loss of bone that supports your teeth. Periodontitis can lead to your gums pulling away from your teeth. This creates pockets that can become infected. Eventually, this can result in tooth loss and possibly have systemic health implications such as those listed above. Periodontitis requires professional treatment, which may include deep cleaning (scaling and root planing), medications, or even surgery, depending on the severity of the condition.
Signs and Symptoms of Gum Disease
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of gum inflammation and disease is crucial as it allows for early detection, intervention, and treatment to prevent further progression of the disease.
The most common signs and symptoms of gum problems include the following:
- Red, Swollen, or Tender Gums. Inflammation is the earliest sign of gum disease. They may appear red and swollen and can be tender to the touch.
- Bleeding Gums. If your gums bleed during brushing, flossing, or even when eating hard food, it could be a sign of gum disease.
- Persistent Bad Breath. Also known as halitosis, this may be an indication of gum disease caused by plaque buildup.
- Receding Gums. If you have exposed roots, it could be a sign that your gums are receding, a common symptom of gum disease.
- Loose or Shifting Teeth. As gum disease progresses, it can cause loss of supporting bone and tissues, causing teeth to loosen or shift.
- Painful Chewing. Discomfort or pain while chewing can be a sign of gum disease.
- Sensitive Teeth. If you notice sudden sensitivity to hot and cold, it may be due to receding gums exposing the sensitive part of your teeth.
- Changes in Bite. Changes in the way your teeth fit together can indicate the progression of gum disease.
How To Keep Your Gums Healthy
Keeping your gums healthy requires proactive care and good oral hygiene practices. When gum health is compromised, it can lead to gum disease, which has been linked to other systemic health issues, as mentioned above.
Here are some key steps and practices for maintaining healthy gums and a healthy mouth overall:
- Brush Regularly. Brush your teeth at least twice daily using a soft-bristled toothbrush and replace it every three to four months, or sooner if the bristles fray.
- Floss Daily. Flossing once a day helps to remove food and plaque from between your teeth and along the gumline where your toothbrush can't reach.
- Use Mouthwash. Ask your dentist about using an antiseptic mouthwash that can help to kill bacteria that cause plaque and gum disease.
- Quit Smoking. Smoking is strongly associated with the onset of gum disease. By quitting smoking, you significantly reduce the risk of developing gum disease and other health conditions.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals and low in sugar can help protect your gums. Consuming plenty of fruits and vegetables can contribute to overall gum health.
- Stay Hydrated. Drinking plenty of water, especially after meals, can help wash out some of the negative effects of sticky and acidic foods and beverages.
- Have regular Dental Check-ups. Visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and exams. This allows your dentist to detect early gum disease symptoms before they become serious.
- Control Diabetes. People with diabetes are more likely to have gum disease. Regular monitoring and controlling blood sugar levels can help prevent complications, including gum disease.
Schedule an Appointment
To learn more about the emphasis Palmetto Dental Arts places on gum health, call us or contact us online.